What is the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve Bank, or ‘Fed’, is the central banking system of the United States. It acts as the primary regulator of the US dollar, as well as the ‘lender of last resort’ for other banks.
Regulatory currency
The Federal Reserve works to maintain the interest rates that banks use to lend money to each other – and by extension – the interest rate you would get when you take a loan from a bank. By regulating interest rates, they work to regulate the money supply. This also gives them some control over how fast the economy grows or shrinks, as well as inflation. One of the Federal Reserve’s missions is to maintain stable prices (which means controlling inflation).
Regulating the economy
When interest rates are low, it is ‘cheaper’ for people and businesses to borrow money, so they will borrow more. When interest rates go up, people take out fewer loans. In general, businesses borrow money when they want to hire new people or increase their production capacity (for example, build a new factory). Most new businesses take out loans to cover start-up costs. This means that if the economy starts to slow down, the Fed will cut interest rates to make it ‘cheaper’ for businesses to start up or expand. If the economy starts to expand too quickly (such as the ‘Tech Bubble’ of the late 1990s), they will raise interest rates to try to slow it down. The Federal Reserve’s other main task is to maximize employment and minimize unemployment. This, combined with controlling inflation, is sometimes called the ‘dual mandate’.
Controlling inflation
Inflation is what happens when prices across the economy go up – typically prices increase by around 3% per year in the United States. One reason for this is cyclical – think if you run your own business. If all the other companies you rely on for supplies raise their prices, you’ll have to raise yours too because of the extra costs. If you want to give your employees a pay rise, either because they are doing a good job or just because you know their cost of living has gone up due to price increases, you will have to pay them more too. Because of the way money is created in the US, this also means that the money supply will generally increase when interest rates are low, and generally decrease when interest rates go up. The Fed also works to maintain a stable inflation rate to prevent prices across the economy from rising too quickly.
Research and development
The Federal Reserve Bank is also the largest economic research organization in the world, employing an army of researchers who investigate everything from economic development to the effects of new currencies on our current money supply. If you want more information about some of the research done by the Federal Reserve, or to access some of the economic data they collect (like GDP), you can visit the St. Louis Federal Reserve page.
Federal Reserve System
Branches
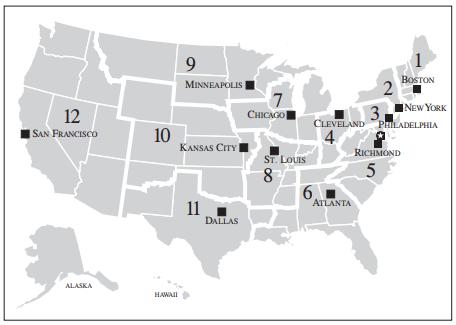
The Federal Reserve Bank is divided into 12 “branches”, each responsible for its own territory. The branches are: – Atlanta – Boston – Chicago – Cleveland – Dallas – Kansas City – Minneapolis – New York – Philadelphia – Richmond – San Francisco – St Louis The branches are distributed according to what the country’s economic activity looked like in 1913 (when the Fed was created) – the Northeast with a greater concentration, with the plains area very spread out. Missouri is the only state to have two Fed branches, mostly because a senator from Missouri, James A. Reed, was instrumental in getting the law that created it to pass the Senate. Some of the branches have special functions – for example, the Federal Open Market Committee, which determines US monetary policy, is chaired by the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (with other Fed branches rotating on 5 other positions on the committee). The New York Federal Reserve Bank also has the world’s largest gold storage facility. Over 95% of the gold stored here comes from other countries as part of their own foreign exchange reserves, representing around 10% of all the world’s gold reserves. Countries store gold at the Federal Reserve for practical reasons – if countries need to trade gold between each other, it is easier to move it from one vault to another within the same facility than to ship it between countries.
Relationships with commercial banks
All banks in the United States are required to hold a ‘reserve requirement’, which means a percentage of deposits that are available for withdrawal and not lent out. Banks can either keep this as cash stored in the bank vault or (much more commonly) deposited with the Federal Reserve Bank. If a bank does not have enough cash to meet its reserve requirement at the end of the day, they must make loans from other banks, or the Federal Reserve itself, and deposit the borrowed money. This feature is why the Federal Reserve Bank is sometimes called the “lender of last resort”, and the interest rate charged for these overnight loans is called the “overnight rate”.
About the Vikingen
With Vikingen’s signals, you have a good chance of finding the winners and selling in time. There are many securities. With Vikingen’s autopilots or tables, you can sort out the most interesting ETFs, stocks, options, warrants, funds, and so on. Vikingen is one of Sweden’s oldest equity research programs.
Click here to see what Vikingen offers: Detailed comparison – Stock market program for those who want to get even richer (vikingen.se)