What is a p/e ratio?
P/E ratio or P/E ratio. It sounds great and makes beginners feel like they have a handle on the situation, but how valuable is the P/E ratio? Surprisingly, the price-to-earnings ratio is a useful tool but certainly not the holy grail of investing it sometimes appears to be. For these beginners, the P/E ratio provides a numerical representation of the value between the share price and earnings. To derive the P/E ratio, you divide the stock price by the company’s EPS or earnings per share. The formula looks like this: P/E = Share price/ EPS
– Market sentiment. An overly optimistic P/E ratio may indicate that the market expects great things from this company. Temper optimism with reality. – Cover priced or overbought. A high value may indicate that a given stock is overpriced and ready for a correction. Be sure to compare against industry norms.
– Lack of self-confidence. A low value may indicate a lack of confidence in the company’s future. – Sleeper. A low value could be a sleeper company just waiting to be discovered.
Formula
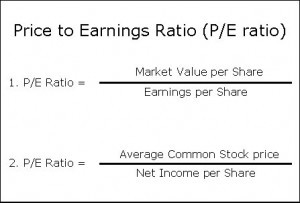
Example
For example, if a company is currently trading at $43 per share and earnings over the past 12 months were $1.95 per share, the P/E ratio for the stock would be 22.05 ($43/$1.95). Coca-Cola and Pepsi operate in the same industry and produce goods that are very similar in nature. Coca-Cola’s (KO:NYSE) stock price (price per share): $66 Coca-Cola’s earnings per share (EPS): $5.26 Coca-Cola’s P/E ratio: $66/$5.26 = 12.55 Pepsi’s (PEP:NYSE) stock price (price per share): $69 Pepsi’s earnings per share (EPS): $3.73 Pepsi’s P/E ratio: $69/$3.73 = 18.50 From our calculations, we can see that Pepsi has a higher P/E ratio than Coca-Cola. This can be perceived in a couple of different ways: – Coca-Cola is undervalued and should be bought. – Pepsi is overvalued and should be sold or shorted – Investors do not feel that Coca-Cola is doing as well as Pepsi at the moment. – Pepsi is launching a new product that Coca-Cola is not. The truth is normally a combination of these perceptions.
How to use P/E ratios?
The P/E ratio itself is just a number. Just because it’s high or low doesn’t provide much intuition on its own. But when we compare P/E ratios across companies and industries, we really start to get a picture of the particular company we are analyzing. It doesn’t make much sense to compare P/E ratios for companies in different industries, because each industry has its own unique way of doing business. It’s like comparing a doctor to an engineer to see which one is more valuable. Therefore, if you are comparing P/E ratios, you should compare between companies in the same or similar industries. You can also compare the P/E ratio of a company with the P/E ratio of the entire industry in which it operates to analyze whether the stock is over or undervalued.
How to interpret the P/E ratio
High P/E ratio may mean: Market sentiment: An overly optimistic P/E ratio may indicate that the market expects great things from this company. The company has high growth potential. Life cycle: The company may be entering the growth or shake-out phase of its life cycle. Industry: Specific industries have a certain level of P/E ratios. For example, most technology companies have high P/E ratios. Overpriced or overbought: A high P/E ratio can indicate that a given stock is overpriced and ready for a correction. This means it may be overvalued. Make sure to compare against industry norms.
Low P/E ratio can mean:
Lack of confidence: A low P/E ratio may indicate a lack of confidence in the company’s future. Life cycle: The company may be in the mature or decline phase of its life cycle. Industry: Specific industries have a certain level of P/E ratio. For example, most energy companies have low P/E ratios.Sleeper: A low P/E ratio can be a sleeper just waiting to be discovered. This means it could be undervalued and a perfect opportunity to start buying the shares.
Important note
– The earnings per share (EPS) in the P/E ratio formula is a number that comes from the company’s accounting records. – Therefore, it is possible to manipulate EPS and thus the P/E ratio to trick investors into perceiving the stock differently. – It is important to independently verify that the company’s financial statements are sound and true.
Conclusion
A P/E ratio is an important valuation tool that can provide important insights into whether a stock may be over- or undervalued. Also sometimes known as “price multiple” or “earnings multiple.”
About the Vikingen
With Vikingen’s signals, you have a good chance of finding the winners and selling in time. There are many securities. With Vikingen’s autopilots or tables, you can sort out the most interesting ETFs, stocks, options, warrants, funds, and so on. Vikingen is one of Sweden’s oldest equity research programs.
Click here to see what Vikingen offers: Detailed comparison – Stock market program for those who want to get even richer (vikingen.se)













