Eight volatility indicators every trader should know
Volatility trading is a great way to take advantage of fast-moving markets. Discover the eight volatility indicators that help you measure and navigate market volatility – so you can make your move when the market changes.
What are volatility indicators?
Volatility indicators are technical tools that help traders and analysts measure and understand the periods of high and low volatility in a particular stock, or the market as a whole. When selecting a stock, traders often look at its historical volatility or its implied volatility to help determine the risks associated with it. It is important for you to understand the different volatility indicators and how to use them – to help you make more informed trading decisions.
How to identify market volatility
To identify market volatility, you need to have a basic understanding of the forces that drive each market. Many traders and analysts use standard deviation as their primary measure of volatility. This measure reflects the average amount a stock’s price differs from the mean over a period of time. You can calculate the standard deviation by using the following formula:
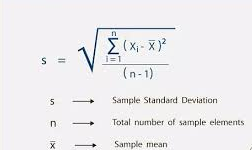
Volatility is often divided into two categories: – Low volatility – the value of a security does not fluctuate dramatically and tends to be more stable – High volatility – the value of a security can change dramatically over a short period of time in either direction Different market conditions require different strategies. While periods of low volatility may be suitable for a more relaxed trading style, periods of high volatility are beneficial for breakout strategies and scalping. Volatility can afflict almost any market, whether driven by macroeconomic events, human psychology or factors unique to a sector. Understanding market conditions can inform your trading decisions – the indicators below can help you identify market volatility.
How to use volatility indicators in trading
1. learn more about the best volatility indicators 2. select the asset you want to trade 3. open an account or log in with your broker, for example DEGIRO, Nordnet, Aktieinvest, Levler and Avanza. 4. Take steps to manage your risk 5. Place your trade
The top eight volatility indicators
1. Bollinger Bands 2. ATR – Average True Range Indicator 3. VIX – Volatility Index 4. Keltner Channel Indicator 5. Donchian Channel Indicator 6. Chaikin volatility indicator 7. Twiggs volatility indicator 8. RVI – Relative Volatility Index * Please note that these are not necessarily the best indicators by any specific measure and using them does not guarantee a positive outcome on your trades. The selected indicators are some of the most useful and popular among traders when it comes to measuring volatility.
Bollinger band
Bollinger Bands are a prominent type of technical price indicator. An upper and lower band, placed on either side of a simple moving average (SMA), make up their structure. Each band can be used to identify regions of support and resistance as it is plotted two standard deviations from the market SMA. Viking automatically calculates the Bollinger Bands for you, but it is still useful for a trader to know what the different bands mean and what can be learned from them.
Pros and cons of Bollinger Bands
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Strong trends produce volatility, as seen when Bollinger Bands widen and narrow, making them valuable trend indicators | Bollinger Bands are a trailing indicator, which means they do not predict price patterns but rather track existing market trends. This means that you may not get signals until the price movement has already started |
| Bollinger Bands are incredibly user-friendly and can give you a different perspective when plotted automatically by a trading software | Bollinger Bands should be used in conjunction with other technical analysis tools, according to their creator John Bollinger, who also noted that they are not flawless or foolproof indicators of market trends. |
ATR – Average True Range indicator
The Average True Range (ATR) indicator is used to track volatility over a given time period. It moves up or down based on how pronounced price changes are for an asset, with a higher ATR value indicating greater market volatility and a lower ATR indicating lower market volatility.
How to calculate Average True Range
To calculate the Average True Range, you must first calculate the true range. You do this by taking the largest of these three calculations: – The current high minus the previous close – The current low minus the previous close – The current high minus the current low You would repeat this process over a specific time frame to get a moving average of a series of true ranges.
Advantages and disadvantages of ATR
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ATR is a smoothed moving average of volatility over a given time frame | The stop-and-reverse mechanism assumes that you switch to a short position when stopping from a long position, and vice versa |
| It can be used in currency, index, stock and commodity markets | Although ATR is useful, you should use it alongside other indicators to confirm forecasts |
| ATR is often used to assess when and where to enter or exit a position, as well as at what price level to implement a trailing or guaranteed stop |
VIX – Volatility Index
The VIX is a real-time volatility index, created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). It was the first benchmark to measure expectations of market volatility. However, because the index is forward-looking, it only shows the implied volatility of the S&P 500 (SPX) over the next 30 days. The VIX is derived as a percentage using the pricing of SPX index options. The S&P 500 is most likely to experience a decline if the VIX value rises, while a decline in the VIX value indicates that the index is likely to be stable.
To calculate the VIX, you must use extremely complex math, although it is not necessary for you to understand this to trade the index.
Go long or short on VIX
| Go long VIX | Go short on VIX |
| You will take a long position on the VIX if you believe that volatility will increase and the VIX will rise. Going long on the VIX is a popular position in times of financial instability, when there is a lot of stress and uncertainty in the market | When you take a short position on the VIX, you are basically expecting the S&P 500 to rise in value. Shorting volatility is especially popular when interest rates are low, there is reasonable economic growth and low volatility in financial markets |
| If there had been volatility, your prediction would have been correct and you could take a profit. If you had taken a long position and there was no volatility in the market, your position would have suffered a loss | If the S&P 500 does indeed rise, the VIX is likely to move to a lower level, and you could take a profit. However, shorting volatility is inherently risky, as there is the potential for unlimited loss if volatility increases |
Keltner channel indicator
The Keltner channel indicator looks for areas of price volatility in an asset. It uses three independent lines to assess an asset’s volatility based on price movements and support or resistance levels. If the asset’s price closes above the upper band, which represents resistance, or below the lower band, which represents support, it could indicate that the trend is either about to change or pick up speed.
Using Keltner channels on MT4
The Keltner channel is one of the most popular indicators on MetaTrader 4 (MT4), mostly used by forex traders as the forex market is quite volatile. It has the feature of automatically applying Keltner Channels to your charts while using the platform. Apart from the Keltner channel, the platform comes with a host of indicators and add-ons, some of which you get for free when you download MT4 from our website.
Donchian channel indicator
The Donchian channel indicator is used by traders to spot possible breakouts and retracements. To clearly map the information from the channel and quickly act on any future trading indications. The price chart below gives an example of what Donchian channel indicators look like when put over a candlestick chart. The middle band reflects an average of the current high and current low for that trading session, while the upper and lower bands represent the highest high and lowest low respectively for the previous period.
Chaikin volatility indicator
The Chaikin volatility indicator shows the difference between the moving averages of two volume-weighted accumulation-distribution lines. Volatility is measured as a widening of the range between a security’s high and low price by comparing the gap between these two prices. An increase in the volatility indicator over a short period may indicate that a bottom is near. An impending top may be indicated by a long-term decline in volatility. The Chaikin indicator should be used in conjunction with a moving average system or price envelope.
How to calculate Chaikin volatility
High Low Average = EMA of (High – Low) Volatility = (High Low Average – High Low Average of n periods ago) / High Low Average of n periods ago] x 100
Twiggs volatility indicator
The Twiggs volatility indicator is used to signal increased market risk. It is used to track market indices such as the Dow and S&P 500 but can also be useful for tracking the behavior of individual stocks.2 Twiggs volatility is most commonly used to indicate rising and falling market risk, where: – Rising troughs show an increase in market risk – Peaks that fall show a decrease in market risk
Relative volatility index (RVI)
The Relative Volatility Index (RVI) was developed by Donald Dorsey, and it calculates the direction of volatility of an asset’s price. The RVI can range from zero to 100 and unlike many indicators that measure price movements, the RVI does an exceptional job of measuring market strength.
RVI buy and sell signals
Below are the rules developed by Dorsey for buying and selling signals when using RVI:4 – Buy if RVI is greater than 50 – Sell if RVI is less than 50 – If you miss the first RVI buy signal, buy when RVI is greater than 60 – If you miss the first RVI sell signal, sell when RVI is less than 40 – Close a long position when RVI falls below 40 – Close a short position when RVI rises above 60 This RVI is not intended to be used as a stand-alone indicator for trading and should be used in combination with other trading tools and methods.
A summary of volatility indicators
– Volatility indicators are technical tools that help traders and analysts measure and understand the periods of high and low volatility in a particular stock or the market as a whole – Many traders and analysts use standard deviation as their primary measure of volatility – Volatility is often divided into two categories or risk – low and high risk – You can trade volatility with stocks, options, ETFs or CFDs
About the Vikingen
With Vikingen’s signals, you have a good chance of finding the winners and selling in time. There are many securities. With Vikingen’s autopilots or tables, you can sort out the most interesting ETFs, stocks, options, warrants, funds, and so on. Vikingen is one of Sweden’s oldest equity research programs.
Click here to see what Vikingen offers: Detailed comparison – Stock market program for those who want to get even richer (vikingen.se)













