Different trading strategies
Trading strategies that work in the foreign exchange market. Forex trading requires you to put together several factors to formulate a trading strategy that works for you. There are many different trading strategies that can be followed, but it is important to understand and be comfortable with the strategy. Each trader has unique objectives and resources, which must be taken into account when choosing the appropriate strategy.
There are three criteria that traders can use to compare different strategies for their suitability:
1. What time resources are required
2. frequency of trading opportunities
3. typical distance to the target
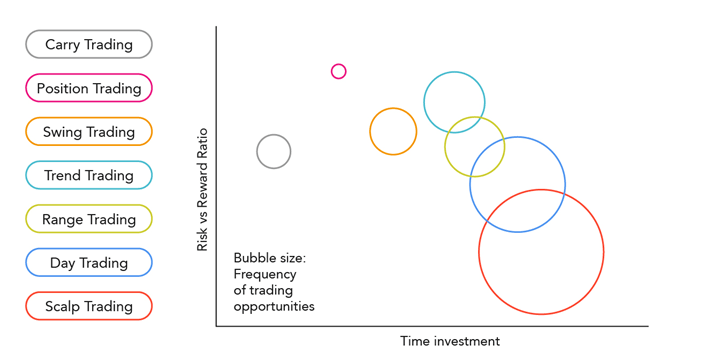
To easily compare the forex strategies on the three criteria, we have compiled them in a bubble chart. On the vertical axis is the ‘Risk-Reward Ratio’ with strategies at the top of the chart having a higher reward for the risk taken for each trade.
Position trading is usually the strategy with the highest risk/reward ratio. On the horizontal axis is time investment which represents the amount of time required to actively monitor trading. The strategy that requires the most in terms of your time is scalping trading because of the high frequency of trades that are regularly placed.
 Price action trading
Price action trading
Price action trading involves the study of historical prices to formulate technical trading strategies. Price measures can be used as a stand-alone technique or in conjunction with an indicator. Fundamental is rarely used; however, it is not uncommon to incorporate economic events as an underpinning factor. There are several other strategies that fall within the price action described above.
Length of trade
Price action trading can be used over different time periods (long, medium and short term). The ability to use multiple timeframes for analysis makes price action trading valued by many traders.
Entry/exit
There are many methods for determining support and resistance levels that are commonly used as entry and exit points:
– Fibonacci retracement
– Using light bodies
– Trend identification
– Indicators
– Oscillators
Within price action there is range, trend, day, scalping, swing and position trading. These strategies follow different forms of trading requirements which will be described in detail below. The examples show different techniques for trading these strategies to demonstrate how diverse trading can be, along with a variety of customized options for traders to choose from.
Interval trading
Range management includes identifying support and resistance points whereby traders will place trades around these key levels. This strategy works well in the market with no significant volatility and no noticeable trend. Technical analysis is the primary tool used in this strategy.
Length of trade
There is no fixed duration per trade as delineated strategies can work in any time frame. Managing risk is an integral part of this approach as breakouts can occur. Consequently, a distance trader wants to close all current range-bound positions.
Entry/Exit
Oscillators are most often used as timing tools. Relative Strength Index (RSI), Commodity Channel Index (CCI) and stochastics are some of the more popular oscillators. Price action is sometimes used in combination with oscillators to further validate range bound signals or breakouts.
Example 1: USD / JPY Range Trading
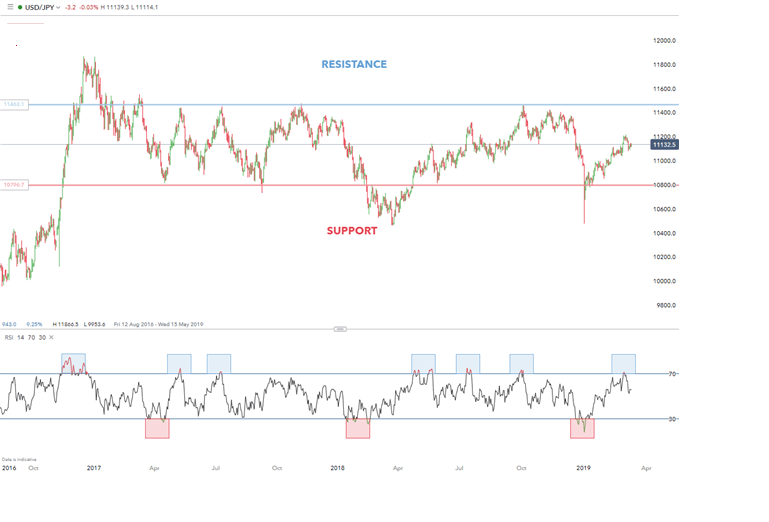 The USD/JPY currency pair has shown a sustained price level in recent years. The chart above illustrates a clear support and resistance band that traders use as entry and exit points. The RSI oscillator shows the timing of entry and exit points marked by the shaded blue and red boxes – blue: overbought and red: oversold.
The USD/JPY currency pair has shown a sustained price level in recent years. The chart above illustrates a clear support and resistance band that traders use as entry and exit points. The RSI oscillator shows the timing of entry and exit points marked by the shaded blue and red boxes – blue: overbought and red: oversold.
Interval trading can result in fruitful risk/reward ratios, but this comes along with long time investment per trade. Use the pros and cons below to align your goals as a forex trader with the amount of resources you have.
Advantages
– Large number of trading opportunities
– Favorable risk/reward
Disadvantages:
– Requires long periods of investment
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical analysis
Trend trading
Trend trading is a simple forex strategy used by many traders of all experience levels. Trend trading seeks to provide a positive return by exploiting the directional force of a market.
Length of trade
Trend trading usually takes place in the medium to long term, while trends themselves vary in length. As with price action, multiple time frame analysis can be used in trend trading.
Entry/Exit
The entry point is usually denoted by an oscillator (RSI, CCI etc) and exit points are calculated based on a positive risk-reward ratio. Using stop-loss distances, traders can either equal that distance or exceed it to maintain a positive risk-reward ratio, e.g. If the stop level was placed 50 pips away, the winnings level is set at 50 pips or more away from the starting point.
Example 2: Identifying the trend
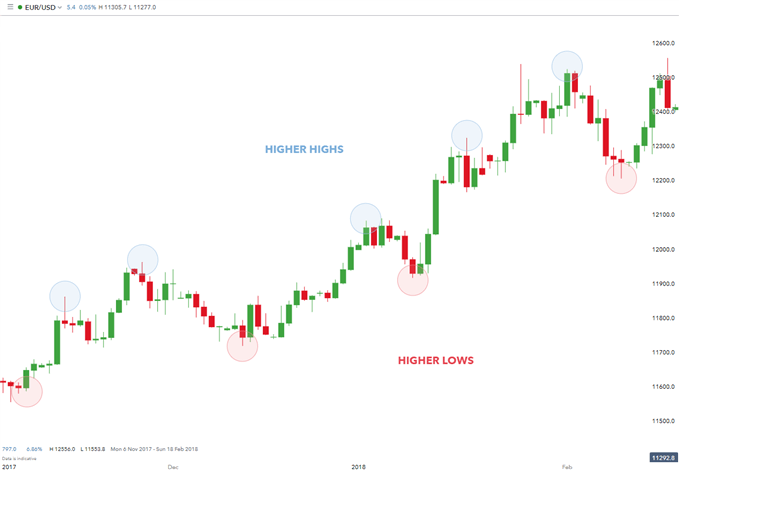 In the simple example above, the EUR/USD currency pair shows an upward trend validated by higher highs and higher lows. The opposite would be true for a downward trend.
In the simple example above, the EUR/USD currency pair shows an upward trend validated by higher highs and higher lows. The opposite would be true for a downward trend.
EUR/USD Let the trend be your friend
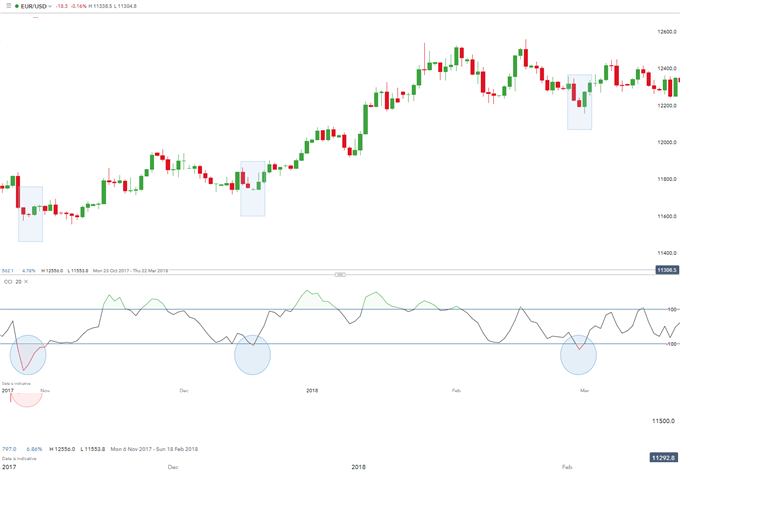 When you see a strong trend in the market, trade the direction of that trend. For example, the strong trend in EUR/USD above.
When you see a strong trend in the market, trade the direction of that trend. For example, the strong trend in EUR/USD above.
Using the (CCI) as a tool to time entries, notice how every time the CCI dipped below -100 (marked in blue), prices responded with a rally. Not all industries will work this way, but as the trend is followed, each dip caused more buyers to enter the market, pushing prices higher. In conclusion, identifying a strong trend is essential for a fruitful trend trading strategy.
Trend trading can be reasonably labor intensive with many variables to consider. The list of pros and cons can help you decide if trend trading is right for you.
Advantages
– Large number of trading opportunities
– Favorable risk/reward ratio
Disadvantages
– Requires long periods of investment
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical analysis
Position trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy that focuses mainly on fundamentals, but technical methods can be used such as Elliot Wave Theory. Minor market fluctuations are not considered in this strategy as they do not affect the broader market picture. This strategy can be used in all markets from stocks to forex.
Length of trade
As mentioned above, position trading has a long-term outlook (weeks, months or even years!) These trades are therefore reserved for the more persistent trader. Understanding how economic factors affect markets or basic technical predispositions is crucial to anticipating trading ideas.
Entry/exit
Key levels on longer time frames (weekly/monthly) contain valuable information for position traders because of the comprehensive view of the market. Entry and exit points can be assessed using technical analysis under the other strategies.
Example 3: Germany 30 (DAX) Position Trading
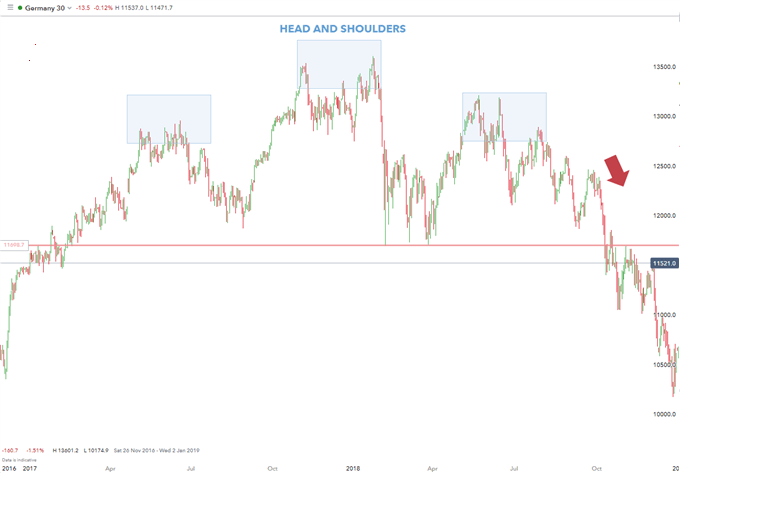 The DAX30 chart above shows an approximate two-year head and shoulders pattern, which is in line with a likely fall below the neck line (horizontal red line) after the right shoulder. In the selected example, the DAX30 played downwards as planned both technically and fundamentally.
The DAX30 chart above shows an approximate two-year head and shoulders pattern, which is in line with a likely fall below the neck line (horizontal red line) after the right shoulder. In the selected example, the DAX30 played downwards as planned both technically and fundamentally.
Towards the end of 2018, Germany went through a technical recession along with the US/China trade war which hurt the automotive industry. The Brexit negotiations did not help matters as the possibility of the UK leaving the EU would likely also affect the German economy. In this case, understanding technical patterns as well as having strong fundamentals allows combining technical and fundamental analysis to structure a strong trading idea.
Advantages
– Requires minimal time investment
– Very positive risk-reward ratio
Disadvantages
– Very few trading opportunities
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical and fundamental analysis
Day trading
Day trading is a strategy designed to trade financial instruments within the same trading day. That is, all positions are closed before the market closes. This can be one or more transactions during the day.
Length of trade
Trading times range from very short term (matter of minutes) or short term (hours), as long as trades are opened and closed within the trading day.
Entry/exit
Traders in the example below look to enter positions at when price breaks through the 8-period EMA in the direction of the trend (blue circle) and exit with a 1:1 reward ratio.
Example 4: Day trading EUR/USD
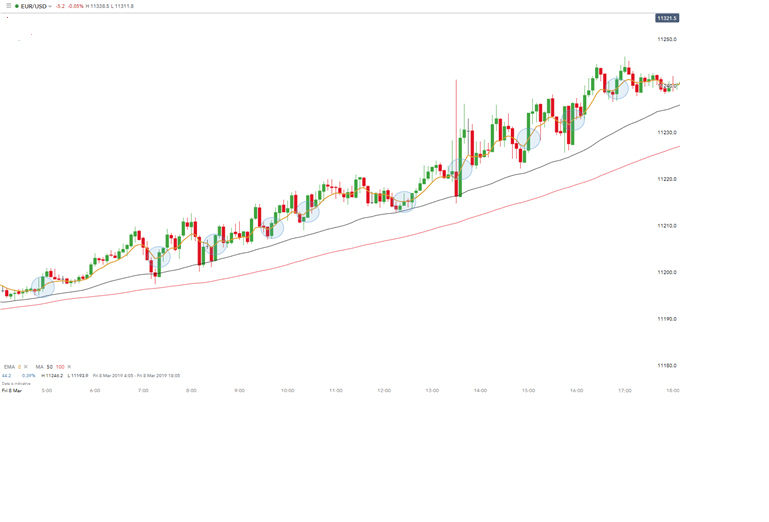 The chart above shows a representative daily setup with moving averages to identify the trend that is long in this case as the price is above the MA lines (red and black). Entry positions are marked in blue with stop levels placed at the previous price break. Take profit levels will correspond to the stop distance in the direction of the trend.
The chart above shows a representative daily setup with moving averages to identify the trend that is long in this case as the price is above the MA lines (red and black). Entry positions are marked in blue with stop levels placed at the previous price break. Take profit levels will correspond to the stop distance in the direction of the trend.
The advantages and disadvantages listed below should be considered before following this strategy. Day trading involves a lot of time and effort for little reward, as shown in the EUR/USD example above.
Advantages
– Large number of trading opportunities
– Median risk/reward ratio
Disadvantages:
– Requires long periods of investment
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical analysis
Scalping
Scalping in forex is a common term used to describe the process of taking home small profits on a frequent basis. This is achieved by opening and closing several positions during the day. This can be done manually or through an algorithm that uses predefined guidelines for when and where to buy and close positions. The most liquid currency pairs are preferred as the spread is generally tighter, making the strategy suitable for the short term.
Length of trade
Scalping involves short-term trades with minimal returns, usually this strategy works on a shorter time horizon (30 min – 1 min).
Entry/Exit
Like most technical strategies, identifying the trend is step 1. Many scalpers use indicators such as MA, moving average, to verify the trend. Using these key levels for the trend on longer time frames allows a forex trader to see the bigger picture.
These levels create support and resistance. Scalping within this band can then be attempted on smaller time frames using oscillators such as RSI. Stops are placed a few pips away to avoid large movements against the trade. The MACD indicator is another useful tool that can be exercised by the trader to go open and close trades.
Example 5: EUR/USD Scalping
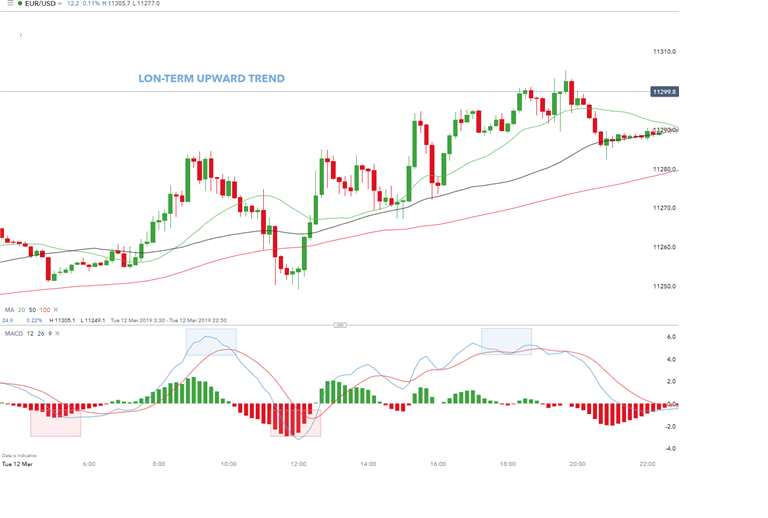 The EUR/USD 10 minutes above shows a typical example of a scalping strategy. The long-term trend is confirmed by the moving average (price above 200 MA). The smaller timeframe is then used to target entry and exit points. The timing of the entry points is shown by the red rectangle in the trader’s bias (long). Traders can also close long positions with MACD when the MACD (blue line) crosses above the signal line (red line) marked by the blue rectangles.
The EUR/USD 10 minutes above shows a typical example of a scalping strategy. The long-term trend is confirmed by the moving average (price above 200 MA). The smaller timeframe is then used to target entry and exit points. The timing of the entry points is shown by the red rectangle in the trader’s bias (long). Traders can also close long positions with MACD when the MACD (blue line) crosses above the signal line (red line) marked by the blue rectangles.
However, traders use the same theory to set up their algorithms but without manual execution by the trader.
With this practical example of scalp trading, use the list of pros and cons below to choose a suitable trading strategy that best suits you.
Advantages
– Highest number of trading opportunities of all currency strategies
Disadvantages
– Requires long periods of investment
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical analysis
– Lowest risk/reward ratio
Swing trading
Swing trading is a speculative strategy whereby traders look to take advantage of both trading patterns and market trends. By choosing ‘tops’ and ‘bottoms’, traders can enter long and short positions accordingly.
Length of trade
Swing trading is considered to work best in the medium term as positions are usually held anywhere between a few hours to a few days. Long-term trends are preferred because traders can take advantage of the trend at several points along the trend.
Entry/exit
Like the bounded strategy, oscillators and indicators can be used to select optimal entry and exit positions and times. The only difference is that swing trading applies to both trend and range bound markets.
Example 6: Trading strategy for GBP/USD
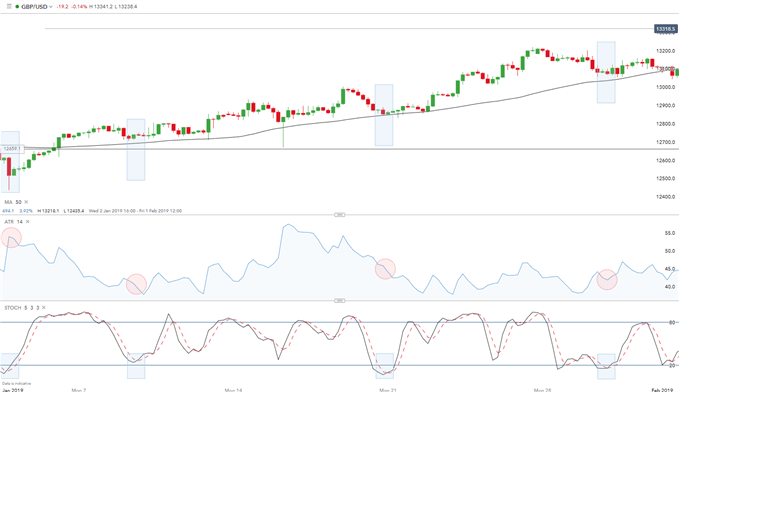 A combination of the stochastic oscillator, the ATR indicator and the moving average was used in the example above to illustrate a typical swing trading strategy. The upward trend was initially identified by the 50-day moving average (price above the MA line). In the case of a trend, traders will look to enter long positions using the old adage of ‘buy low, sell high’.
A combination of the stochastic oscillator, the ATR indicator and the moving average was used in the example above to illustrate a typical swing trading strategy. The upward trend was initially identified by the 50-day moving average (price above the MA line). In the case of a trend, traders will look to enter long positions using the old adage of ‘buy low, sell high’.
Stochastics are then used to identify entry points by looking for oversold signals marked by the blue rectangles on the stochastics and chart. Risk management is the final step where the ATR gives an indication of stop levels. The ATR figure is marked by the red circles. This figure represents the approximate number of pips away the stop level should be set.
For example, if the ATR shows 41.8 (reflected in the latest ATR reading) the trader would look to place stops 41.8 pips away from entry. We recommend that you trade with a positive risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2. This would mean setting a take profit level (limit) at least 83.6 (41.8 x 2) away or beyond.
Once you’ve seen an example of swing trading in action, consider the following list of pros and cons to decide if this strategy is right for you.
Advantages
– Large number of trading opportunities
– Median risk/reward ratio
Disadvantages
– Achieves strong appreciation of technical analysis
– Significant time investment is still required
Carry trades
Carry trades involve a currency trader borrowing (selling) a currency at a lower interest rate, followed by investing (buying) in another currency at a higher interest rate. This will ultimately lead to positive trade. This strategy is mainly used in the foreign exchange market.
Length of trade
Carry trades depend on the interest rate differentials between the associated currencies, therefore the duration of these trades is medium to long term (weeks, months and possibly years).
Entry/Exit
Strong trending markets work best for carry trades because the strategy involves a longer time horizon. Confirmation of the trend should be the first step before starting such a deal (higher highs and higher lows and vice versa).
There are two aspects to a carry trade, namely currency risk and interest rate risk. Consequently, the best time to open the positions is at the beginning of a trend to fully exploit the exchange rate changes. Regarding the interest rate component, this will remain the same regardless of the trend as the FX trader will still receive the interest rate differential if the first named currency has a higher interest rate against the second named currency, e.g. a higher rate of interest than the first named currency. AUD/JPY.
Can carry trades work for you? Consider the following pros and cons and see if it is a forex strategy that suits your trading style.
Advantages
– Some time to make the investments is needed
– Median ratio of risk to reward
Disadvantages
– Picking up strong appreciation of the foreign exchange market
– Few trading opportunities
Trading strategies for the forex market
This article describes 8 types of forex strategies with practical trading examples. When considering a trading strategy to follow, it can be useful to compare the amount of time investment required behind the monitor, the risk-reward ratio and the accuracy of the overall trading opportunities.
Each trading strategy will appeal to different traders depending on personal attributes. Matching trading personality with the appropriate strategy will ultimately enable traders to take the first step in the right direction.
About the Viking
With Viking’s signals, you have a good chance of finding the winners and selling in time. There are many securities. With Viking’s autopilots or tables, you can sort out the most interesting ETFs, stocks, options, warrants, funds, and so on.
Click here to see what Vikingen offers: Detailed comparison – Stock market program for those who want to become even richer (vikingen.se)













