Five types of Elliott Wave Patterns to understand market behavior
Elliott Wave Pattern- Do you know that these patterns can help you understand market behavior? Yes! That is absolutely true! But before we get into patterns let’s actually understand what the Elliott wave principle is: The Elliott wave principle is a form of technical analysis that helps traders analyze financial market cycles. Using this Elliott wave theory, traders can predict market trends by identifying extremes in prices and investor psychology. Elliott Wave Theory suggests that market movements follow a sequence of crowd psychology cycles. Elliott Wave Pattern is formed according to the ongoing market sentiment, which alternates between bullish and bearish cycles. However, Elliott Wave should not be considered as a technical indicator but a theory that helps to predict market behavior. In this blog, we will discuss the five main types of Elliott Wave Pattern that help the traders to predict the market behavior:
What is Elliott Wave Theory?
Elliott Wave Theory proposes that stock prices move continuously up and down in the same patterns called waves formed by the psychology of traders. The theory holds, as these are recurring patterns, the movements of stock prices can be easily predicted. Investors can get an insight into ongoing trend dynamics as they observe these waves and also help in deeply analyzing the price movements. But traders should note that the interpretation of the Elliot wave is subjective as investors interpret it in different ways. Before discussing the patterns, let’s discuss motives and corrective waves: What are motives and corrective waves? The Elliott wave can be categorized into motifs and corrective waves:
1. motive waves
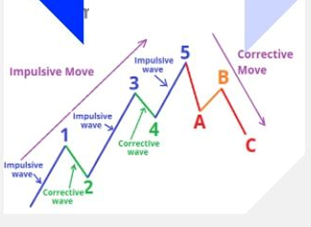
Motif waves move in the direction of the main trend and consist of 5 waves labeled as Wave 1, Wave 2, Wave 3, Wave 4 and Wave 5. Wave 1, 2 and 3 move in the direction of the main trend while wave 2 and 4 move in the opposite direction. There are usually two types of subject waves – impulse waves and diagonal waves.
2. Corrective waves
Waves that counteract the main trend are known as the corrective waves. Corrective waves are more complex and time consuming than motive waves. Corrective patterns consist of three waves and are labeled as A, B and C. The three main types of corrective waves are Zig-Zag, Diagonal and Triangle Waves. Now let’s get to Elliott Wave Patterns: Below are the 5 main types of Elliott Wave Patterns
1. impulse
Impulse is the most common motive wave and also the easiest to detect in a market. Like all motif waves, the impulse wave has five sub-waves: three motif waves and two corrective waves that are labeled as a 5-3-5-3-5 structure. But the formation of the wave is based on a set of rules. If any of these rules is broken, the impulse wave is not formed and we must relabel the suspected impulse wave. The three rules for impulse wave formation are: Wave 2 cannot trace more than 100% of wave 1. Wave 3 can never be the shortest of waves 1, 3 and 5. Wave 4 can never overlap wave 1. The main goal of a motive wave is to move the market and impulse waves are best at accomplishing this.
2. diagonal
Another type of motive wave is the diagonal wave which, like all motive waves, consists of five sub-waves and moves in the direction of the trend. The diagonal looks like a wedge that can either expand or contract. In addition, the sub-waves of the diagonal may not have a number of five, depending on the type of diagonal observed. Like other motif waves, each sub-wave of the diagonal wave does not go all the way back to the previous sub-wave. In addition, sub-wave 3 of the diagonal is not the shortest wave. Diagonals can be further divided into end and leading diagonals. The ending diagonal usually occurs in wave 5 of an impulse wave or the last wave of corrective waves, while the leading diagonal is found in either wave 1 of an impulse wave or the wave A position of a zigzag correction.
3. zig-zag
Zig-Zag is a corrective wave consisting of 3 waves labeled as A, B and C that move sharply up or down. The A and C waves are motivational waves while the B wave is corrective (often with 3 sub-waves). Zigzag patterns are sharp declines in a bull rally or advances in a bear rally that significantly correct the price level of the previous Impulse patterns. Zigzags can also form in a combination known as double or triple zigzags, where two or three zigzags are connected by another corrective wave between them.
4 Platt
The flat is another three-wave correction where the sub-waves are formed in a 3-3-5 structure which is labeled as an A-B-C structure. In the flat structure, both wave A and B are corrective and wave C is motif with 5 sub-waves. This pattern is known as the flat when it moves sideways. Generally, within an impulse wave, the fourth wave has a flat while the second wave rarely does. On the technical charts, most flats usually do not look clear because there are variations on this structure. A flat may have a wave B terminating after the start of the A wave and the C wave may terminate after the start of the B wave. This type of flat is known as the extended flat. The extended flat is more common in markets compared to the regular flats discussed above.
5. triangle
The triangle is a pattern consisting of five sub-waves in the form of a 3-3-3-3-3 structure, which is labeled as A-B-C-D-E. This corrective pattern shows a balance of forces and it moves sideways. The triangle can either be expanding, with each of the following sub-waves getting bigger, or contracting, that is, in the form of a wedge. The triangles can also be categorized as symmetrical, descending or ascending, based on whether they point sideways, upwards with a flat top or downwards with a flat bottom. Subwaves can form in complex combinations. It may theoretically look easy to spot a triangle, it may take some practice to identify them in the market. As we have discussed above, the Elliott Wave Pattern is open to interpretations in different ways by different traders, so are their patterns. Thus, traders should make sure that when they identify the patterns.
About the Vikingen
With Vikingen’s signals, you have a good chance of finding the winners and selling in time. There are many securities. With Vikingen’s autopilots or tables, you can sort out the most interesting ETFs, stocks, options, warrants, funds, and so on. Vikingen is one of Sweden’s oldest equity research programs.
Click here to see what Vikingen offers: Detailed comparison – Stock market program for those who want to get even richer (vikingen.se)













